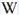Database of luminescent minerals
DIAMOND (French name: DIAMANT )
Chemical formula: C
Family: Native elements
Status: IMA-GP
Crystal system : Isometric
Display mineral: OUI
Luminescence:
Longwave UV (365nm) colors: |
Blue , Bluish White , Yellowish White , Pinkish White , Pale Yellow , Yellow , Dark Orange /Tawn , Red , Salmon pink , Greenish Yellow , Green , Blue , Greenish white , Yellowish , | ||
Intensity LW:Strong | Frequency LW:Often | ||
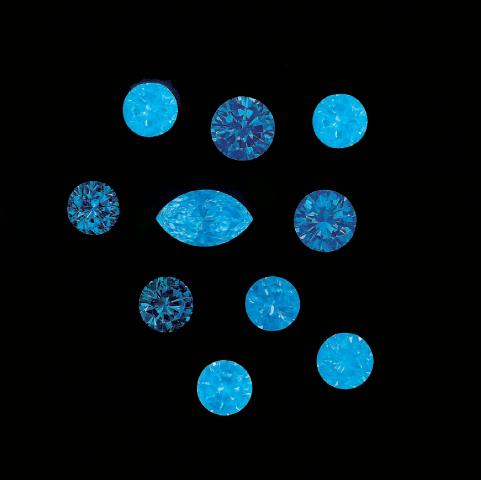
Daylight picture

Diamant, Congo;
Photo et col. G. Barmarin
Longwave (365nm) picture

Diamant UVLW (superbright 2000), Congo;
Photo et col. G. Barmarin
Pictures Galery:


 ...
...  Go to the galery (21 pictures)
Go to the galery (21 pictures)
Do you have a photo of this mineral you would like to see in the gallery? Contact us!
Phosphorescence (in the common sense of the term) observable with the naked eye:
Type d'UV |
Couleur |
Intensité |
Fréquence d'observation |
|---|---|---|---|
UV longs (365nm): | Bluish White | Strong | Often | UV courts (254 nm): | Red | Strong | Very rarely |
Triboluminescence: OUI
Thermoluminescence: OUI
Comments:
Probably the earliest phosphorescent mineral known after exposition to the sunlight. In 1663, Robert Boyle first noted the triboluminescence of diamond when broken. Blue or red Triboluminescence can be observed when sawing a diamond during the cutting process. Mrs. Kunz wife of the well-known mineralogist possessed a prodigious diamond that was phosphorescent in the dark for some minutes after just being exposed to a small pocket electric lamp. Kunz in 1895 attributed the fluorescence and phosphorescence that is shown by some diamonds to the presence of a hypothetical hydrocarbon, for which e gave the name tiffanyite. About One natural diamond upon four is luminescent. Natural blue diamond are semi-conductors and emits light when electrical current is passed through it (electroluminescence).
Activator(s) and spectrum:
Activator(s): N (Azote), B (Bore),
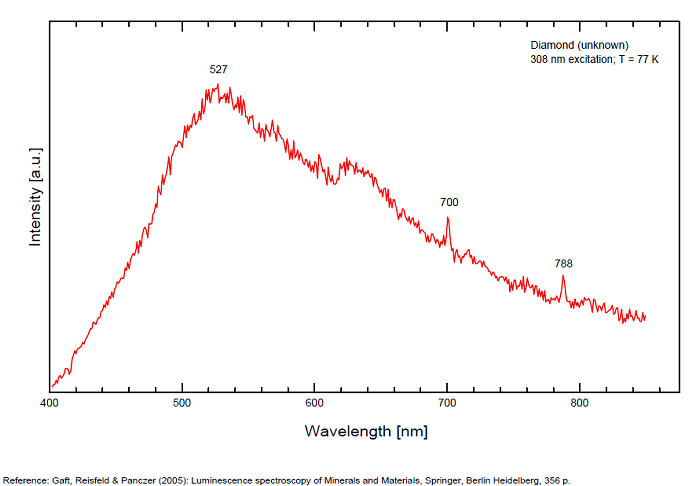
Peaks in the spectrum (nm):
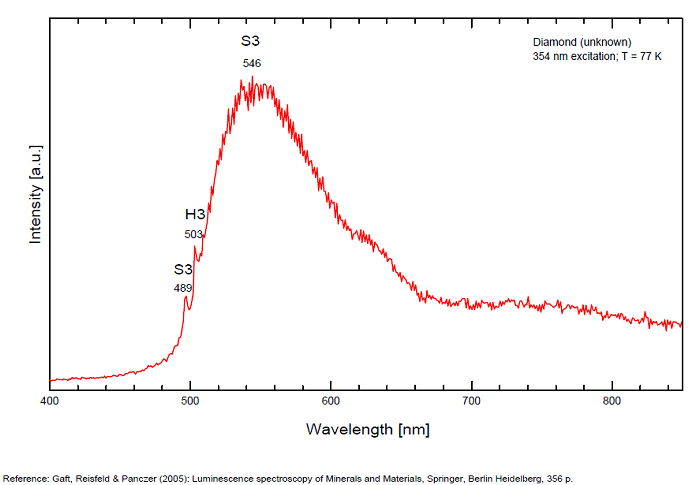
N3 center: 442, 507 nm
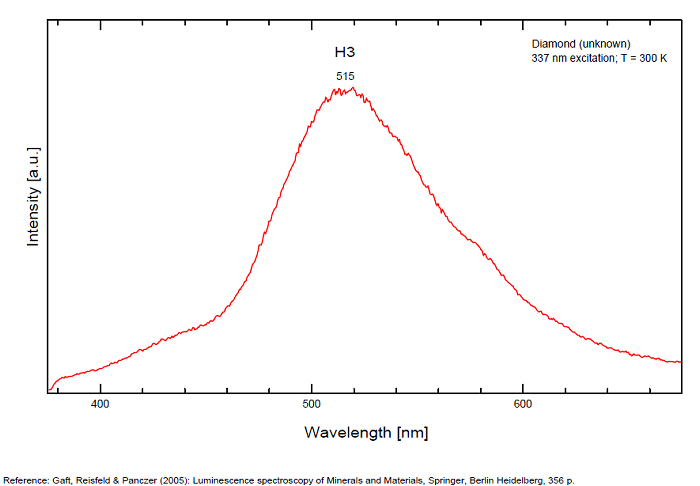
H3 center: 520nm
A-band center: 452nm
N3 center: 415, 428, 439, 452, 731nm

Spectrum Galery:
 ...
...Comments on spectrum and activators:
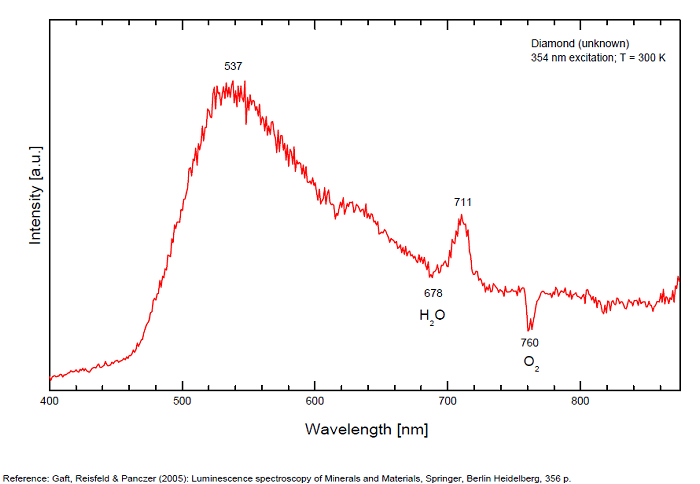
From more than 100 detected centers only for seven the models are determined, mainly based on EPR interpretations. The model includes identification of the impurity, vacancy, interstitial atom, their aggregations and their crystallochemical position together with quantum-chemical and spectroscopic description. (Gaft) Luminescence of diamond is related to various defects in its structure, almost always related to N (Nitrogen) atoms. It is logical, because the atomic radii of C and N are nearly equal (approximately 0.77 Å). N3 center: color and luminescence center attributed to 3 Nitrogen atoms bounded to the same Carbon atom or a vacancy. The luminescence spectra of this center is associated with a large peak at 440-450nm with a fine structure (peaks around 415, 428, 438 and 451nm) a lifetime: 30-40ns and an absoption energy of 2,985eV but other centers (Al imputity for exemple) contribute to this spectrum even if it is not possible aboce 170K to discriminate their contribution. H3 and H4 centers: 496, 506, 512nm ; two Nitrogen atoms coupled with a vacancy in two different configurations. Absorption energy: 2,463eV. Decay-time: 15-20ns S1 center: a combination of one vacancy with one Nitrogen atom, 541nm S2 center: a combination of two vacancies with one Nitrogen atom, 565nm S3 center: a combination one vacancy with several Nitrogen atom H3, H4, S2 and S3 centers are characterized by broad bands at 520-545nm with very weak lines at 489nm and 523nm (S2), 498nm (S3) and 503nm (H3) A-band at 480nm observed in natural diamond of type I A-band with a maximum at 440 nm in natural diamond of type II (low Nitrogen diamonds) Some blue diamonds exhibit a remarkable red phosphorescence such as Hope or Wittelsbach-Graff (both of Indian origin) and Blue Moon (South Africa Cullinan Mine); All natural, untreated type IIb blue diamonds (diamond without Nitrogen but containing some uncompensated Boron) show a phosphorescence with two emission bands: one at 660 nm and another at 500 nm but for those three diamonds, unlike usually, it is the blue that decreases more quickly than the red causing this magnificent red phosphorescence. Type IIb diamonds with orange-red phosphorescence are more commonly originated in India or Venezuela but not in the case of the blue Moon coming from the Cullinan Mine in South Africa where diamond are normally found with a more typical brief bluish phosphorescence. After exposure to short-wave ultraviolet light, the Blue Moon display orange-red phosphorescence (around 660nm) that remain visible for up to 20 seconds. (see bibliography: Eloise Gaillou, Gems and Gemmology, Winter 2014)
Best localities for fluorescence (*):
- Mbuji Mayi, Kasaï-Oriental, DR Congo
(*)The data are not exhaustive and are limited to a few remarkable localities for fluorescence
Bibliographic reference for luminescence:
- The Henkel Glossary of Fluorescent Minerals, Dr. Gerhard Henkel, Published by the FMS, 1989 ,
- Fluorescence: Gems and Minerals Under Ultraviolet Light, Manuel Robbins, 1994, Geoscience Press, ISBN 0-945005-13-X ,
- The World of Fluorescent Minerals, Stuart Schneider, Schiffer Publishing, 2006, ISBN 0-7643-2544-2 ,
- Luminescence Spectroscopy of Minerals and Materials, M. Gaft, R. Reisfeld, G. Panczer, Springer Editor, ISBN: 10 3-540-21918-8 ,
- Luminescent Spectra of Minerals, Boris S. Gorobets and Alexandre A. Rogojine, Moscow, 2002 ,
- Handbook of Fluorescent Gems and Minerals, a practical guide for the gem and mineral collector, Jack de Ment, 1949 ,
Reference for luminescence on the Internet:
- Luminescence/phosphorescence of the "Blue Moon" Diamond, Eloise Gaillou, Gems and Gemmology, Winter 2014;
- A Gemological Study of a Collection of Chameleon Diamonds, Thomas Hainschwang, Dusan Simic, Emmanuel Fritsch, Branko Deljanin, Sharrie Woodring, and Nicholas DelRe, GIA
Videos:
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=l81qETV_5xQ
- The phosphorescing diamond: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Hu3Xs7Fj_u8
- How does fluorescence affect the look of a diamond? https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XY5_neHP5aU
Mineralogical reference on the Internet:
 http://www.mindat.org/show.php?name=Diamond
http://www.mindat.org/show.php?name=Diamond
 http://webmineral.com/data/Diamond.shtml
http://webmineral.com/data/Diamond.shtml
Internet Search:
 Image search on 'Google Images'
Image search on 'Google Images'
 Search for documents in all languages on Google
Search for documents in all languages on Google
A request providing no result means only that no such reference exists in the database, but it does not mean that what you are looking for does not exist, just not to our knowledge. If you think you have found an error or omission, please let us know via the contact page being sure to cite the source of information.